What Happens At The Cathode
I presume y'all are referring to the electrolysis of copper (Ii) sulfate with copper electrodes. During the electrolysis of copper (Two) sulfate, or
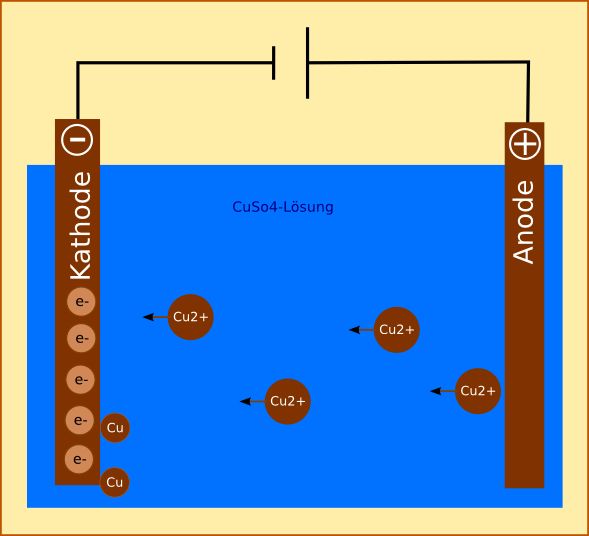
It is very important to make a stardom between the labelling of the cathode in electrolysis and in galvanic cells, as near of the time this causes a bit of confusion. In electrolysis, the cathode is the negative electrode, while in galvanic cells it acts as the positive electrode.
This deviation is determined by the fact that in electrolysis, an electric current is used to bulldoze a chemical reaction; yet, in a galvanic prison cell, the opposite is true - a chemical reaction is used to produce an electric current.
And so, this is what happens during the electrolysis of
When a straight current (DC) is practical, the cations will be attracted by the cathode and the anions will be attracted past the anode. Here's what takes place at the cathode:
Hither'southward what takes identify at the anode:
In time, this volition ensure that the anode volition dissolve, and that the cathode will increment in size. The concentration of the copper (Two) sulfate solution will remain unchanged during electrolysis.
Here'south a great video on the electrolysis of copper (II) sulfate:
What Happens At The Cathode,
Source: https://socratic.org/questions/what-happens-on-the-cathode-during-the-electrolysis-of-a-copper-ii-sulfate-solut
Posted by: randolphhavall.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Happens At The Cathode"
Post a Comment